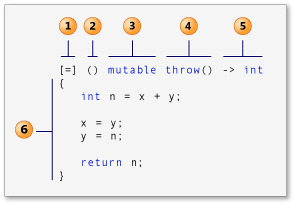
웹 소켓으로 float 형을 보내고 받는 예제를 만들어 달라고 gpt에 요청했더니
처음보는 객체...? 메소드가 보여서 검색
그런데 push 하면 안느리려나? 조금 걱정되네
Int32Array나 Float32Array로 좀더 해보고 안되면 DataView로 해봐야겠다.
socket.onmessage = function(event) {
const data = event.data;
const floatData = [];
const intData = [];
const floatSize = 4; // float32는 4바이트
const intSize = 4; // int32는 4바이트
const floatArrayLength = 4;
const intArrayLength = 4;
const view = new DataView(data);
// float32 배열 추출
for (let i = 0; i < floatArrayLength; i++) {
floatData.push(view.getFloat32(i * floatSize, true));
}
// int32 배열 추출
for (let i = 0; i < intArrayLength; i++) {
intData.push(view.getInt32(floatArrayLength * floatSize + i * intSize, true));
}
document.getElementById("floatData").textContent = JSON.stringify(floatData);
document.getElementById("intData").textContent = JSON.stringify(intData);
}; |
[링크 : https://chatgpt.com/share/fb063d40-1441-457c-a209-0f594d2c482d]
[링크 : https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/DataView/DataView]
[링크 : https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/DataView/getFloat32]